SSH credentials
SSH public key authentication relies on asymmetric cryptography to generate a public and private key pair. The public key remains on the target (remote) machine, while the private key (and passphrase) is stored in Tower as a credential. The key pair is used to authenticate a Tower connection with your SSH-enabled environment.
All credentials are (AES-256) encrypted before secure storage and not exposed in an unencrypted way by any Tower API.
Create an SSH key pair
To use SSH public key authentication:
- The remote system must have a version of SSH installed. This guide assumes the remote system uses OpenSSH. If you are using a different version of SSH, the key generation steps may differ.
- The SSH public key must be present on the remote system (usually in
~/.ssh/authorized_keys).
To generate an SSH key pair:
- From the target machine, open a terminal and run
ssh-keygen. - Follow the prompts to:
- specify a file path and name (or keep the default)
- specify a passphrase (recommended)
- Navigate to the target folder (default
/home/user/.ssh/id_rsa) and open the private key file with a plain text editor. - Copy the private key file contents before navigating to Tower.
Create an SSH credential in Tower
-
From an organization workspace: navigate to the Credentials tab and select Add Credentials.
-
From your personal workspace: select Your credentials from the user top-right menu, then select Add credentials.
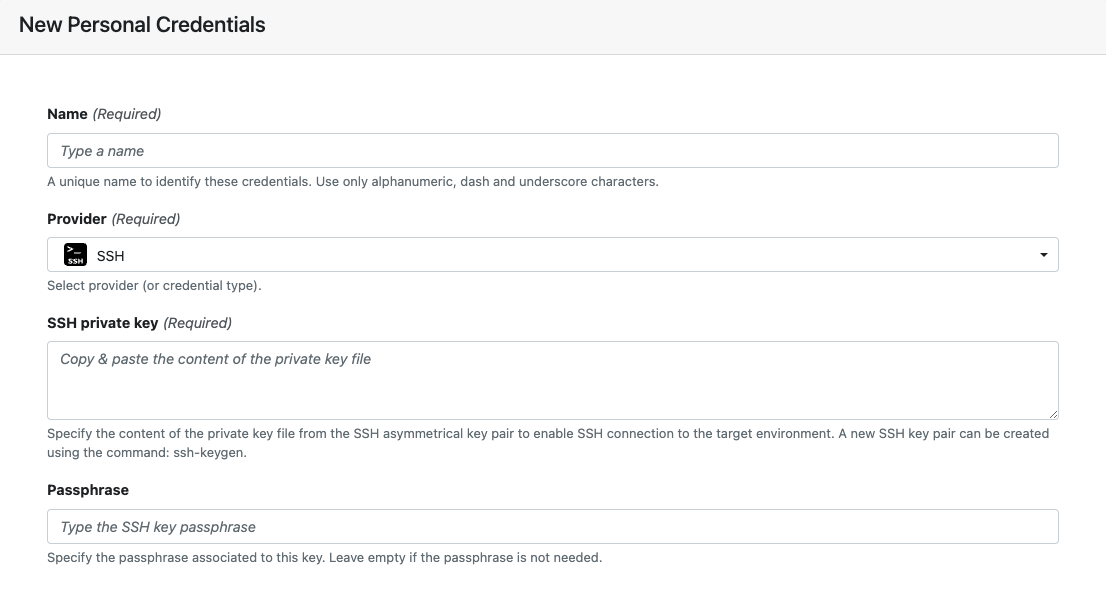
| Property | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Name | A unique name for the credentials using alphanumeric characters, dashes, or underscores. | my-ssh-creds |
| Provider | Credential type | SSH |
| SSH private key | The SSH private key file contents. | -----BEGIN OPENSSH PRIVATE KEY-----b3BlbnNza.... |
| Passphrase | SSH private key passphrase (recommended). If your key pair was created without a passphrase, leave this blank. |
Once the form is complete, select Add. The new credential is now listed under the Credentials tab.